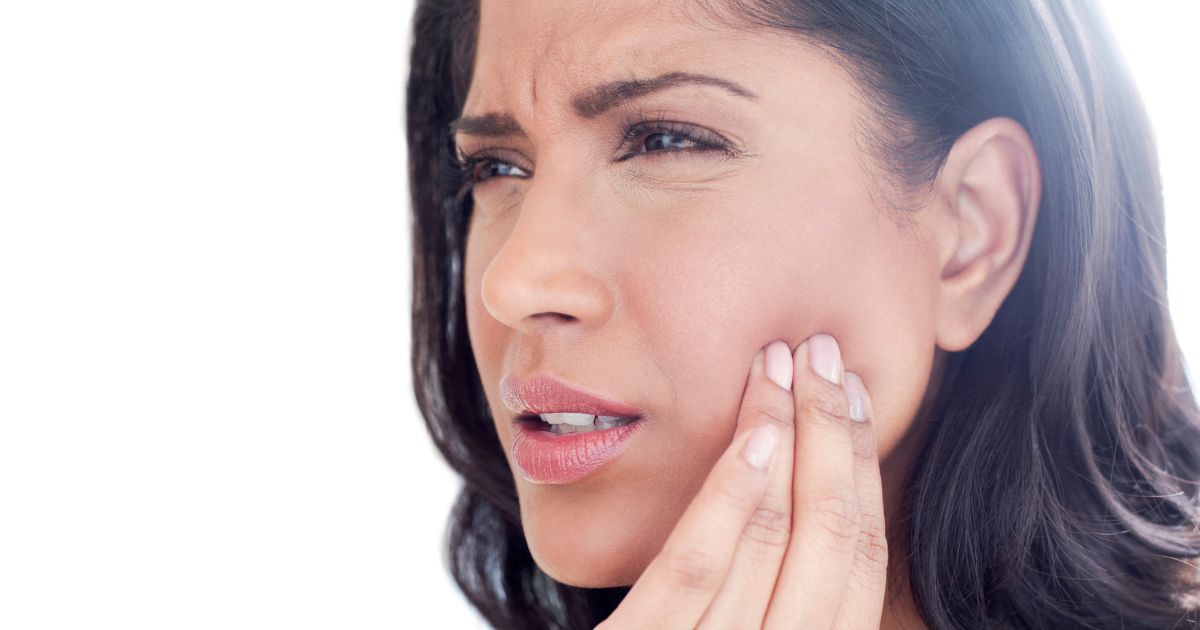
TMJ disorders refer to dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint that connects the two parts of the jaw and makes it possible to open and close the mouth. When these joints do not function properly, smiling, laughing, speaking, eating, and yawning can become problematic. Severe TMJ disorder can make it difficult to chew or even open the mouth wide enough to bite. Common symptoms of TMJ disorder include some or all of the following:
- Clicking or popping of the jaw joint
- Earaches without the presence of infection
- Facial pain
- Difficulty opening the mouth
- Dizziness
- Headaches
- Neck, shoulder, or back pain
- Tooth sensitivity or pain
- Teeth that are cracked, worn, or loose
- Ringing in the ears
What Causes TMJ Disorders?
TMJ disorder occurs when the joint cartilage is damaged by arthritis, the jaw suffers blunt force trauma that damages the joint, when the muscles surrounding the joint are too fatigued to perform their stabilizing function, or when the discs between the joint are damaged or misaligned. An estimated five to twelve percent of the adult population suffer from some form of TMJ disorder, and most of them develop symptoms between the ages of 20 and 40.
There are a number of scenarios that can produce the above problems. Grinding the teeth or clenching the jaw causes the muscles to become fatigued. Stress can be a big factor in teeth grinding and clenching.
An accident that impacts the face can damage the joint, such as when the jaw gets broken or dislocated.
Another common cause of TMJ disorder is malocclusion or a bad bite. When the teeth do not fit together while resting, stress on the hard and soft tissues of the jaw leads to damage to the joint.
Diagnosis and Treatment of TMJ Disorders
When you visit an oral surgeon, they can diagnose TMJ disorder through a physical examination of your face and jaw, including feeling the jaw joint as it is moving, testing your range of motion when opening and closing your mouth, and feeling your face and jaw to see where any pain originates. You can expect to have X-rays taken. If necessary, a CT scan or MRI may be done to get a better look at the jaw joint and surrounding tissue.
TMJ symptoms can be treated with pain relievers, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen, muscle relaxers for those who grind or clench their teeth, or antidepressants, which can aid in deep sleep and relaxation.
For some patients, nonsurgical treatments such as mouth guards, physical therapy, and steroid or Botox injections may prove helpful; for other, more serious cases, surgery may be the best path to relief. Severe cases of TMJ disorder can last years and cause chronic pain if left untreated.
Our South Jersey Oral Surgeons at Lanzi Burke Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeons Diagnose and Treat TMJ Disorders
If you are suffering from any of the symptoms listed above, you may have a TMJ disorder. Lanzi Burke Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeons can help you find relief. Call 856-582-4222 or contact us online today to schedule a consultation with one of our experienced South Jersey oral surgeons. Located in Washington Township, Haddonfield, and Woolwich Township, New Jersey, we serve patients throughout South Jersey.